Describe an Addition Reaction Using Simple Organic Molecules
Although there are only 20 amino acids they can combine to form. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions elimination reactions substitution reactions pericyclic reactions rearrangement reactions and redox reactions.

Addition Reaction Electrophilic Nucleophilic Free Radical Addition Reaction With Faqs
Two molecules become one.

. An elimination reaction is one in which a. Addition reaction any of a class of chemical reactions in which an atom or group of atoms is added to a molecule. It allows ethene molecules to join together to form a single product so it.
An addition reaction in organic chemistry is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one the adduct. Simple sugars such as glucose. Polymers are made up of many repeating units.
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. A B C. Notice that C is the final product with no A or B remaining as a residue.
Heat light and transportation. Compounds with double bonds can undergo addition reactions. Polymers are long chain molecules made by joining many small molecules monomers.
Inorganic Redox Reactions Organic Redox Reactions Oxidation Levels of Organic Compounds 171B 17-5 Carbon Oxidation Numbers Definitions of Organic Oxidation and Reduction Presentation of Redox Reactions in this Chapter 172 Oxidation of Alcohols and Aldehydes 17-6 Oxidation Using CrVI Reagents 172A 17-6. Up to 24 cash back Types of Reactions in Organic Chemistry. A protein consists of many amino acids joined together to form a chain figure 216bc.
In this type of reaction monomer molecules are added to a growing polymer chain one at a time. Addition Reactions An addition reaction is a reaction in which an atom or molecule is added to an unsaturated molecule making a single product. You can hand-draw the structures and copypaste in the lab report sheet or draw the structures using some software freely available.
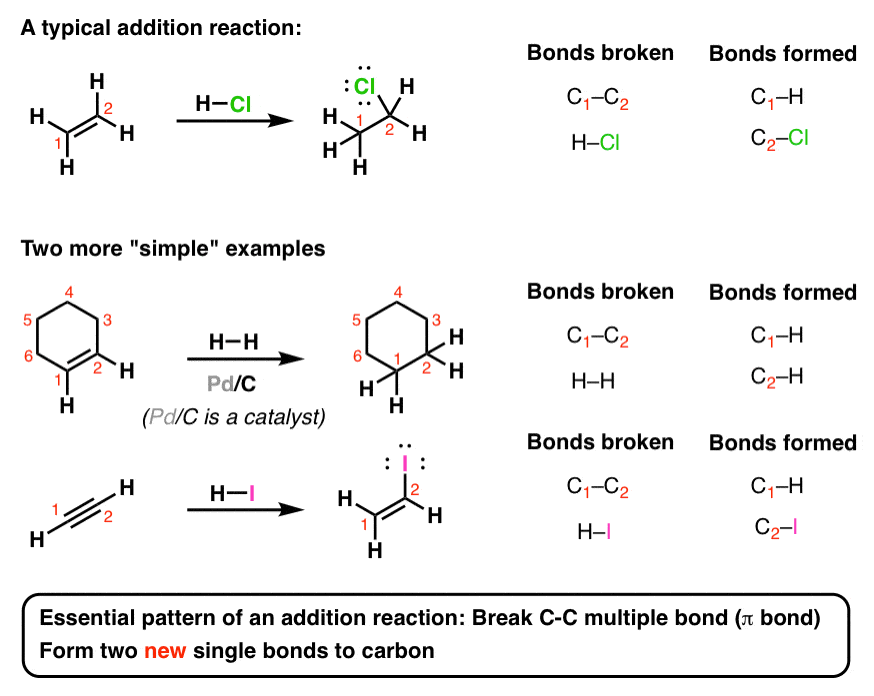
Up to 24 cash back Some Families of Organic Compounds OL Page 3 of 6 G. Examples In an addition all parts of the adding reagent appear in the product. A π bond is broken in an addition reaction.
An organic molecule is a molecule that contains carbon atoms generally bonded to other carbon atoms as well as hydrogen atoms. In an reaction elements of the starting material are lost and an bond is formed. 12 pt OH OH он.
In organic chemistry the most common use of addition reactions involves alkenes. An elimination reaction occurs when a reactant is broken up into two products. Four major examples of addition polymers are polyethylene polypropylene polyvinylchloride PVC and polystyrene see table below.
One type of addition reaction is called hydrogenation. Most of the carbon found in organic molecules originates from inorganic carbon sources such as carbon dioxide captured via carbon fixation by microorganisms. Addition reactions are limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds such as molecules with carboncarbon double bonds alkenes or with triple bonds alkynes and compounds that.
A simple organic molecule propane can be used in a gas lamp left. Galvin Polymerisation reactions are also a type of addition reaction. Addition reactions occur with unsaturated compounds.
Describe preparation of the following compounds starting from a simple organic compound using organometallic chemistry you learned in the lab. A hydration reaction involves the. We look at the patterns and how to name the reactions according to IUPAC rule.
Addition reactions are typical of unsaturated organic compounds ie alkenes which contain a carbon-to-carbon double bond and alkynes which have a carbon-to-carbon triple bondand aldehydes and ketones which have a carbon-to-oxygen double bond. In organic chemistry an addition reaction is an organic reaction in which two or more molecules combine to generate a bigger one the adduct. In organic synthesis organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules.
Elimination reactions occur with saturated compounds. An addition reaction can often be thought of as adding a molecule across the double bond of an alkene or carbonyl or across the triple bond of an alkyne. The production of many man.
The general term used to describe an organic compound containing only C and H atoms is _____. There are 20 basic types of amino acids. Addition Reactions Addition reactions occur when two starting materials add together to form only one product with no atoms left over.
The CC double bond in ethene is involved in the polymerisation reaction. Molecules with carbonhetero double bonds such as carbonyl CO or imine CN groups can be added because they have double-bond character as well. Products of the addition reactions of ethene with chlorine.
The general equation for an addition reaction. Inorganic compounds make up 115 of a living cells mass. -explain what is meant by an addition reaction -write balanced equations using structural formula for the reactions of the alkenes with hydrogen chlorine bromine water and hydrogen chloride -outline the industrial importance of.
Our society depends on combustion reactions for providing some of our most basic needs. No small molecules are eliminated in the process. Inspired by the unique profile of photoredox systems based on light irradiation and the utility of ball milling in mechanochemistry we hypothesized that redox activation of small organic molecules could be achieved through a mechanistically distinct approach using mechanical energy 1922Specifically we envisioned that the agitation of piezoelectric.
Alkenes are molecules consisting of hydrocarbons hydrogen. Additionally combustion reactions have strong cultural power for many people who have grown up with the idea of a comforting hearth backyard barbecues campfires and warm meals and drinks. Hydrohalogenation involves the addition of a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom to an unsaturated.
All four of these organic polymers are also plastics. They are small simple compounds that play important roles in the cell although they do not form cell structures. Addition reactions with unsaturated compounds - leading to saturated compounds.
The complex organic molecule DNA carries the genetic code of a person and can be used to identify them. Humans can synthesize 12 of them from simple organic molecules but the remaining 8 so-called essential amino acids must be obtained in the diet. Halogenation is very similar to hydrohalogenation but a diatomic halogen molecule is added across the.
No comments for "Describe an Addition Reaction Using Simple Organic Molecules"
Post a Comment